Understanding Time Zones in Sql Server
From Dates
Go to text →
Difference Between datetime2 and datetimeoffset
CREATE TABLE #DateTests (DateTime_2 DATETIME2(7), DateTime_Offset DATETIMEOFFSET(7));
INSERT INTO #DateTests VALUES (GETDATE(), GETDATE());
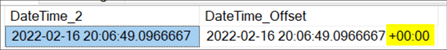
SELECT * FROM #DateTests;
How to add a valid time zone to a datetime value
AT TIME ZONE will assign a time zone offset to a datetime, smalldatetime, or datetime2 value that otherwise would not include one.
It works by simply adding the words AT TIME ZONE immediately after a datetime or datetime2 value and then listing a valid time zone.
This time zone is a NVARCHAR(256) type.
Since this author is writing this tip from the Eastern Time zone in the US, that will be the time zone selected.
The second option is to use the GETUTCDATE() function which will return the UTC date and time rather than the system date and time.
This will be recorded with the correct time zone (+00:00) and will thus be accurate.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS #DateTests;
CREATE TABLE #DateTests (DateTime_2 DATETIME2(7), DateTime_Offset DATETIMEOFFSET(7));
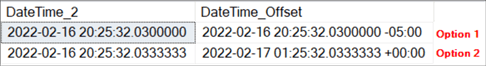
INSERT INTO #DateTests VALUES (GETDATE(), GETDATE() AT TIME ZONE N'US Eastern Standard Time');
INSERT INTO #DateTests VALUES (GETDATE(), GETUTCDATE());
SELECT * FROM #DateTests;
Get list of valid time zones
SELECT * FROM sys.time_zone_info;
Get list of your values for each timezone
SELECT
DateTime_Offset
, tzi.name
, DateTime_Offset AT TIME ZONE tzi.name AS ConvertedDateAndTime
FROM #DateTests
CROSS JOIN sys.time_zone_info tzi
ORDER BY tzi.name;