Data Warehouse Etl Framework
My primary use case for indexed views is using them to mirror data warehouse tables. I do not allow anybody that is not a data engineer access to the original tables. Not even on a read only basis. I create the index views for reports analyst. These are people that know SQL, but have no need to see the audit columns used to run the database.
-- https://tutorials.massstreet.net/v/transact-sql/advanced-topics/lesson-36.-indexed-views
ETL Developers Field Guide
Python Software Engineering Considerations
Use Yaml configuration files for python Etl
Directory Permissions
You should use a Proxy to run Python just like you would SSIS. The Windows account that is being used for the credential has to be explicitly named in the folder permissions. For me, I was in dev and was confused because I was an administrator and administrator was named. It had to be my specific login.
Absolute File Paths
When executing from SQL Server Agent, your script actually executes at C:\WINDOWS\system32. That means you can't use os.getcwd() as the base of file paths. Instead, if you use absolute paths, everything works fine.
EDW ETL Overview
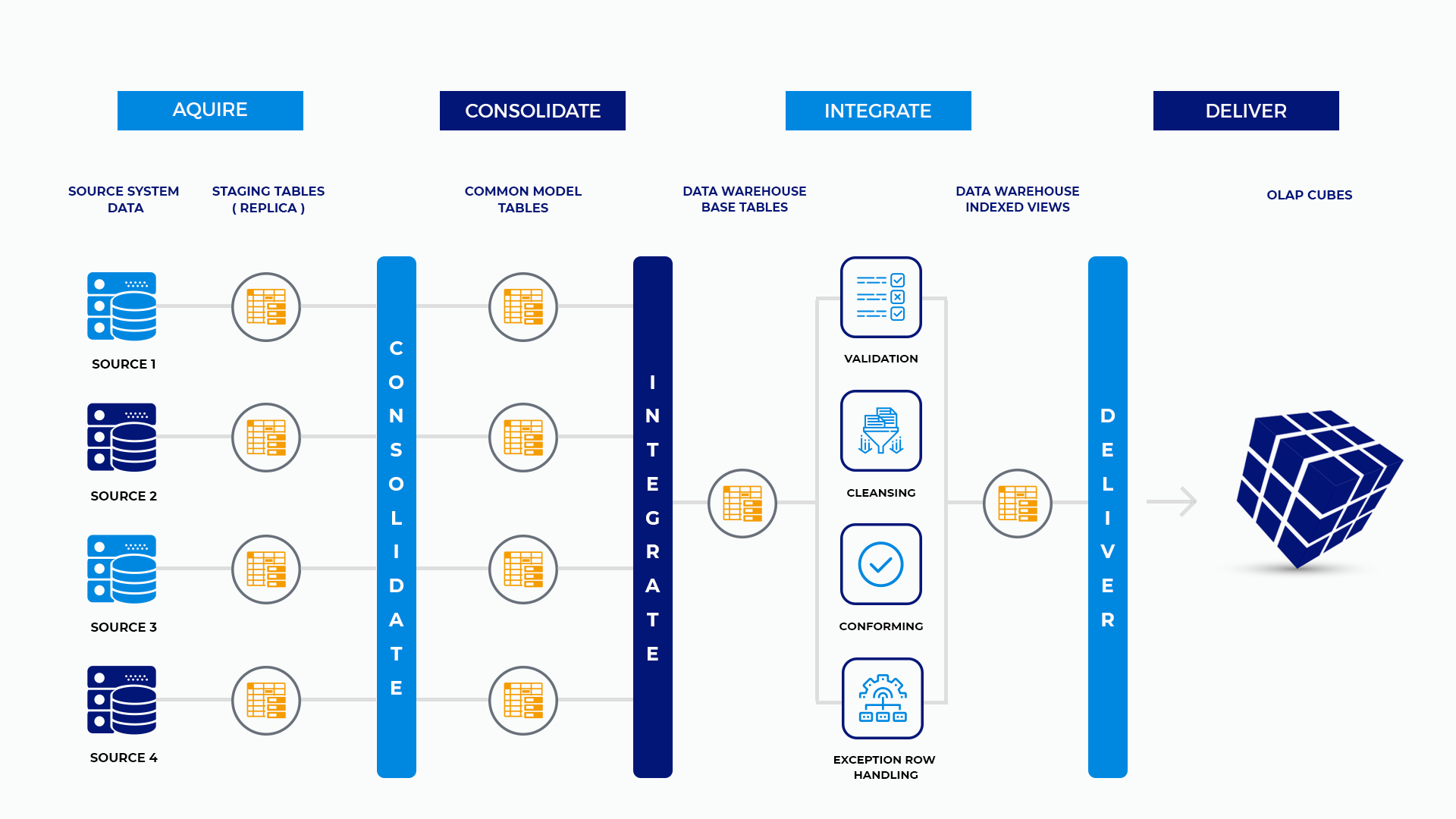
Acquire
Each ETL process that pulls data into the system is entirely independent of any other process. Each dataset is pulled from its source system and placed in a staging table.
Consolidate
All data that is collected in staging tables is moved to common model tables together. The common model is a unified representation of all data across systems.
Integrate
Moving data from consolidate to integrate is accomplished in the same step as moving from acquire to consolidate. Integrate is where we move the data from the common model into the warehouse tables.
Deliver
At this time, there are no OLAP cubes in the data architecture. Data is delivered through various vectors. Most of those vectors pass through the warehouse. A few bypass the warehouse and go straight to de-normalized reporting tables.
ETL Environment Databases
EDW: The Data WarehouseODS: Operational Data Store- This is where all ETL functions take place.
- It is where staging tables and the tables that support the common model live.
- The stored procedures that perform ETL live here as well as any views that support monitoring of the ETL processes.
- This database is not accessible to business users.
REPORTING:- The database consists of de-normalized reporting tables and views that are built from tables in the data warehouse.
- This database allows rapid access to data without having to build complex reports.
- Every model in production, is represented here as a de-normalized view.
SSISManagement:- SSISManagment is the database that holds the logging information from the execution of SSIS packages.
- This database is FAR more useful and user friendly than the execution information provided by SQL Server.
Data Acquisition Paradigms
Demand Pull
- trigged by the data warehouse environment.
- The grand majority of your processes should be demand pull.
- Demand pull is when the system reaches out to other systems on a schedule defined by whatever is stet in your specific orchestration tool.
- The key element being that the data warehouse box has access to the remote system.
- For example, a database to database pull that is executed via a linked server.
Supply Push
- Supply push processes are initiated by processes external to the data warehouse.
- The general scenario here is data is usually dropped by a 3rd party into a folder that sits on an edge server.
- That folder is then scanned by data warehouse processes and moved into the
InterfacesAndExtractsfolder. - Supply push processes should be rare and only done when there are no other options.
- A good example are bank feeds like bank reconciliation files.
- Those are published are published by the bank and the data warehouse does not have the ability to pull the data from the source system.
The Common Model
The common model represents the unified data model for the enterprise. The common model is necessary to process master data.