Nmap
Details
Port scanning tool
Usage
nmap <IP subnet / address> [switches]
With no switches like this the default behavior of Nmap is to Ping and send a TCP Ack packet to ports 80 and 443 to determine whether a host is present.
If you want to perform only host discovery, you can use nmap -sn (or -sP in earlier versions) to suppress the port scan.
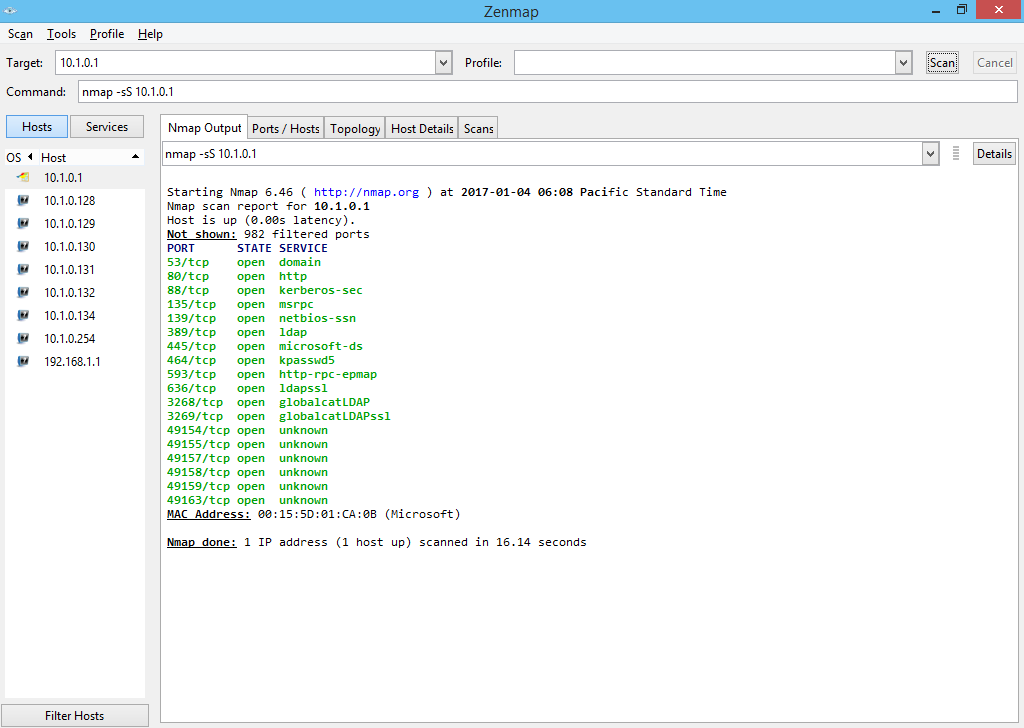
Port scanning
- TCP Syn (
-sS)- This is a fast technique (also referred to as half-open scanning) as the scanning host requests a connection without acknowledging it.
- The target's response to the scan's Syn packet identifies the port state.
- TCP connect (
-sT) - UDP scans (
-sU) - Port range (
-p)- By default, Nmap scans 1,000 commonly used ports.
- Use the
-pargument to specify a port range. - You can also use
--top-portsn, where n is the number of commonly used ports to scan. - The frequency statistics for determining how commonly a port is used are stored in the Nmap-services configuration file.