3ad
Defines the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
From LACP
Go to text →
Resources
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) 3ad
Used to detect configuration errors and recover from the failure of one of the physical links.
Modes
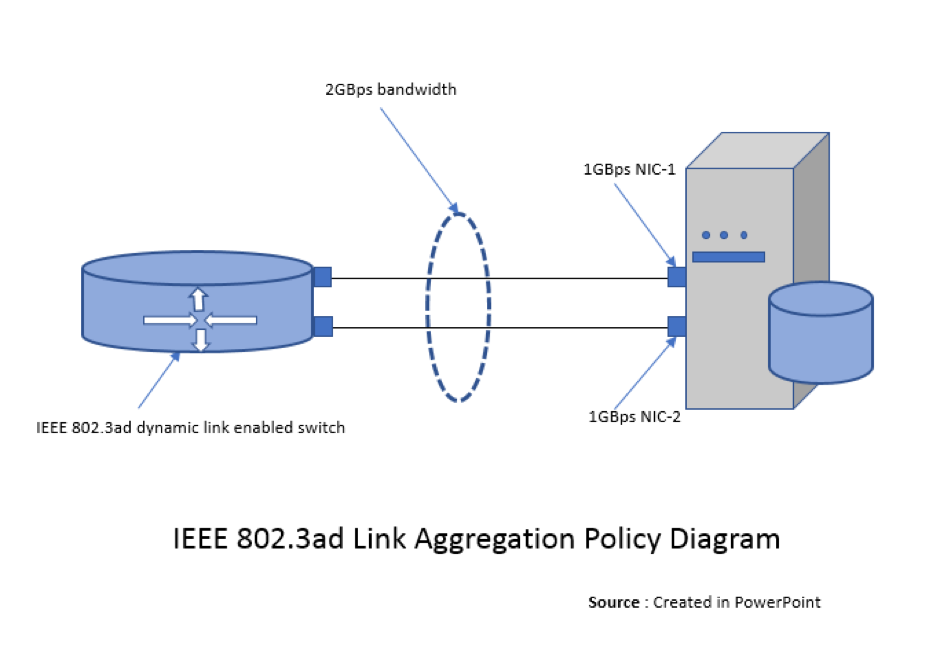
Mode 0 (balance-rr):This mode is also known as round-robin mode. Packets are sequentially transmitted and received through each interface one by one. This mode provides load balancing functionality.Mode 1 (active-backup):This mode has only one interface set to active, while all other interfaces are in the backup state. If the active interface fails, a backup interface replaces it as the only active interface in the bond. The media access control (MAC) address of the bond interface inmode 1is visible on only one port (the network adapter), which prevents confusion for the switch.Mode 1provides fault tolerance.Mode 2 (balance-xor):The source MAC address uses exclusive or (XOR) logic with the destination MAC address. This calculation ensures that the same slave interface is selected for each destination MAC address.Mode 2provides fault tolerance and load balancing.Mode 3 (broadcast):All transmissions are sent to all the slaves. This mode provides fault tolerance.Mode 4 (802.3ad):This mode creates aggregation groups that share the same speed and duplex settings, and it requires a switch that supports an IEEE 802.3ad dynamic link.Mode 4uses all interfaces in the active aggregation group. For example, you can aggregate three 1 GB per second (GBPS) ports into a 3 GBPS trunk port. This is equivalent to having one interface with 3 GBPS speed. It provides fault tolerance and load balancing.Mode 5 (balance-tlb):This mode ensures that the outgoing traffic distribution is set according to the load on each interface and that the current interface receives all the incoming traffic. If the assigned interface fails to receive traffic, another interface is assigned to the receiving role. It provides fault tolerance and load balancing.Mode 6 (balance-alb):This mode is supported only in x86 environments. The receiving packets are load balanced through Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) negotiation. This mode provides fault tolerance and load balancing.
Backlinks